Changes in Global Sepsis Incidence and Mortality
SUMMARY:
-
Recent evidence demonstrates a surge in sepsis incidence and death globally.
-
Several factors may be contributing to this rise.
-
There are age and geographical variances in sepsis cases and death.
REVIEW:
- Source: Global Burden of Disease, Injuries, and Risk Factor Study of 2021
-
- Lancet Glob Health 2025 Published Online October 21, 2025 https://doi.org/10.1016/ S2214-109X(25)00356-0
-
- Trends in the incidence of sepsis and mortality by age group and country from 1991 to 2021
-
- Evaluation of 249 million hospital admissions
-
- Data reported on:
-
-
- Sepsis incidence – overall and per 100,000 population
-
-
-
- Sepsis mortality – overall and per 100,000 population
-
- Data reported for 1990; 2019 and 2021.
- Evaluations of sepsis included by:
-
- Age
-
- Geographic location
-
- Infectious causes
-
- Non-infectious causes
- Between 1990 and 2021, sepsis rates have increased globally
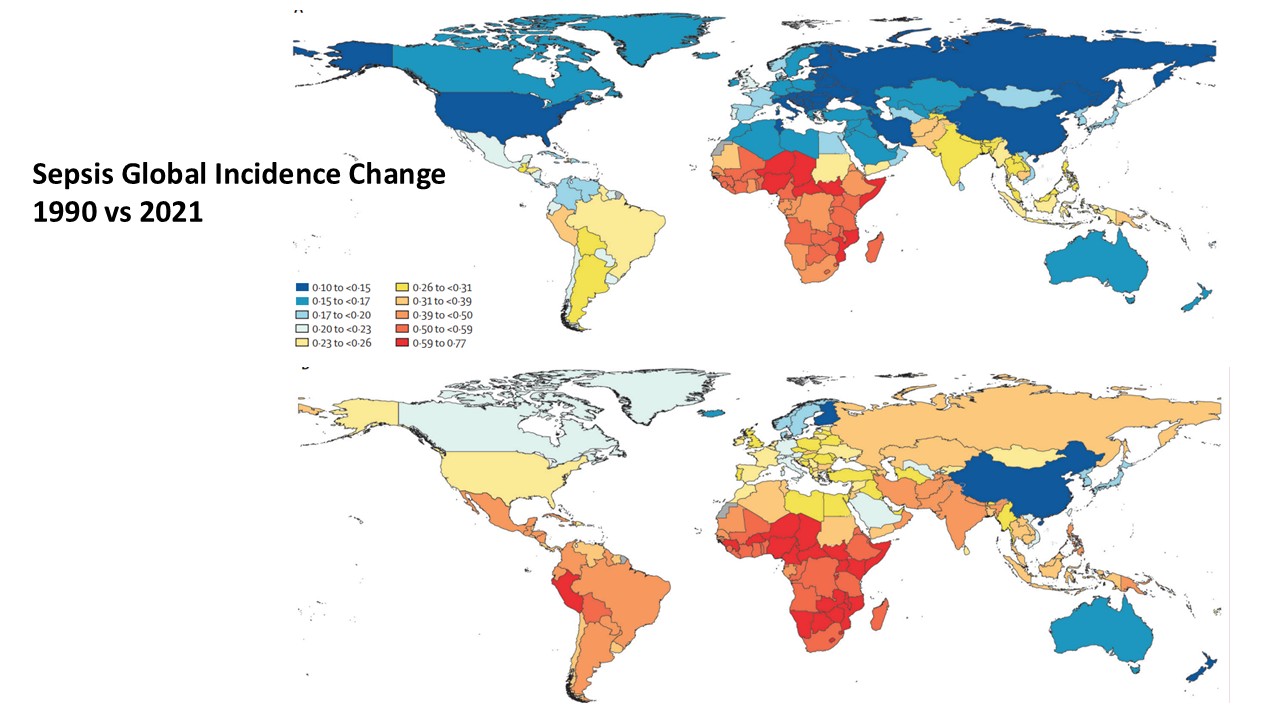
- The areas with the highest incidence of sepsis are:
-
- Sub-Saharan Africa
-
- Latin America
-
- Caribbean
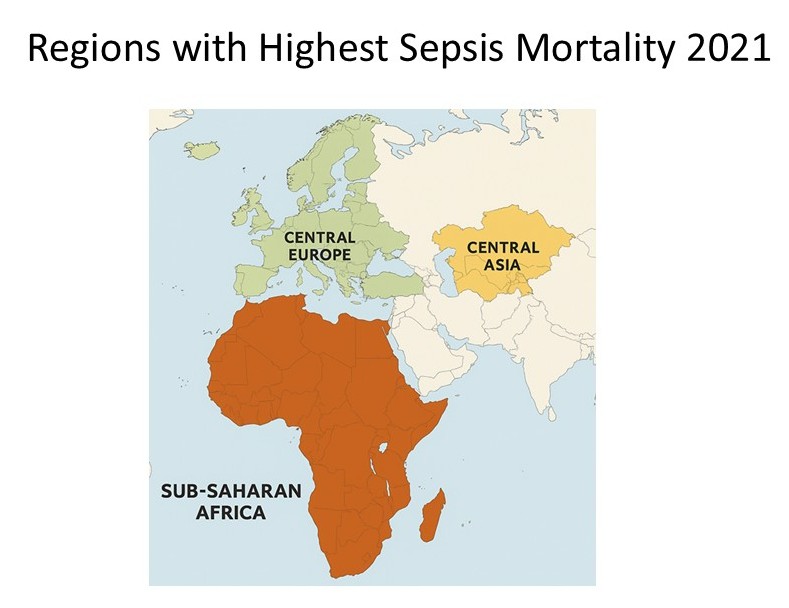
- The areas with the highest sepsis mortality are:
-
- Sub-Saharan Africa
-
- Central Europe
-
- Eastern Europe
-
- Central Asia

- Diseases associated with non-infectious sepsis deaths were:
-
- Stroke
-
- COPD
-
- Type 2 Diabetes
-
- Ischemic heart disease
-
- Colorectal cancer
- Age groups observed changes in the incidence and mortality rates of sepsis.
-
- Children less than 5 years of age showed decreased incidence and mortality rates.
-
- Children 5 – 14 years of age showed modest but plateaued changes.
-
- Adults 15 years and older were the group with increasing incidence and mortality rates of sepsis.
-
- Adults 50 years and older demonstrated the greatest increases in sepsis.

- Possible explanations for the rise in sepsis cases and mortality:
-
- Growing problem of antimicrobial resistance
-
- An aging population
-
- Multiple chronic diseases (over 70% of patients have 2 or more chronic diseases)
-
- The rise may be the late impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
CONCLUSIONS:
- The incidence of sepsis and its associated mortality rates are rising globally.
- Neonate and younger children’s rates are improving, whereas older adult rates are increasing
- This may reflect a post-COVID-19 rise.
To receive articles like these in your Inbox, you can subscribe to Sepsis Program Optimization Insights.
Erkan Hassan is the Co-Founder & Chief Clinical Officer of Sepsis Program Optimization where he designs & oversees the implementation of solutions to optimize sepsis programs.
To discuss your organization’s Barriers of Effective Sepsis Care, contact Erkan by phone (844) 4SEPSIS (844-473-7747), email (erkan@spo.icu), or video chat.





