Is “Metabolic Resuscitation” the Next Step in Sepsis Management?
SUMMARY:
-
Sepsis identification and management remain a global challenge.
-
Metabolic resuscitation has become an area of focus as a therapeutic strategy to address mitochondrial function to counter sepsis-induced organ dysfunction and improve survival.
-
The efficacy of a combined therapy including corticosteroids, Vitamin C, and Thiamine in sepsis patients has produced varied results.
REVIEW:
- The pathophysiology of sepsis is an intricate response between inflammatory responses, dysfunction of the immune system, alterations in neuroendocrine function, coagulation abnormalities, and mitochondrial damage.
- These disruptions all contribute to sepsis
- The mitochondrial dysfunction plays a critical role in the development of sepsis and multiorgan dysfunction syndrome.
- Metabolic resuscitation is a recent attempt to restore the energy balance at a cellular level and address mitochondrial dysfunction.
- Several micronutrients have been suggested to help mitigate the mitochondrial dysfunction. These include:
-
- Vitamin C
-
- Thiamine
-
- Vitamin E
-
- Selenium
-
- Zinc
-
- Coenzyme Q
-
- L-carnitin
-
- Cytochrome oxidase
-
- Melatonin
- Interest has been generated with the triple combination of Vitamin C, Thiamine, and corticosteroids.
Corticosteroids
- The use of corticosteroids in sepsis has been controversial for decades.
- Corticosteroids may reduce the expression of pro-inflammatory markers.
- Corticosteroids may also blunt the inflammatory response.
- The debate over corticosteroids continues due to study design variations:
-
- Small, uncontrolled studies
-
- Different agents
-
- Differing doses
-
- Different time of administration
VITAMIN C
- Vitamin C offers antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulation properties.
- Early studies of small scale and observational in nature have reported positive findings (usually in combination with corticosteroids and thiamine).
- Recent larger randomized trials of Vitamin C alone have resulted in conflicting results.
- Vitamin C monotherapy was found ineffective in impacting sepsis 28-day mortality (35.4% Vit C vs 31.6% in placebo).
-
- Organ dysfunction was longer in the Vitamin C group.
- Vitamin C was also found to be ineffective when combined with hydrocortisone.
Thiamine
- Thiamine can provide a protective effect on mitochondrial activity.
- Thiamine deficiency also contributes to the development of lactic acidosis.
- Thiamine also plays a role in antioxidant pathways.
- The use of thiamine and vitamin C combinations may restore organ function in patients with sepsis and septic shock.
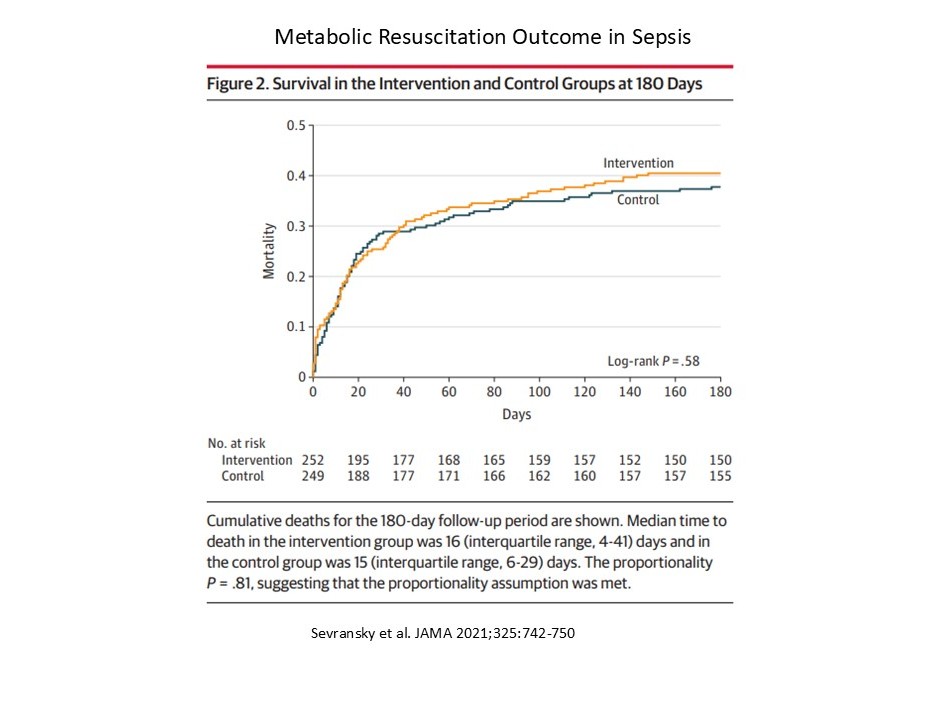
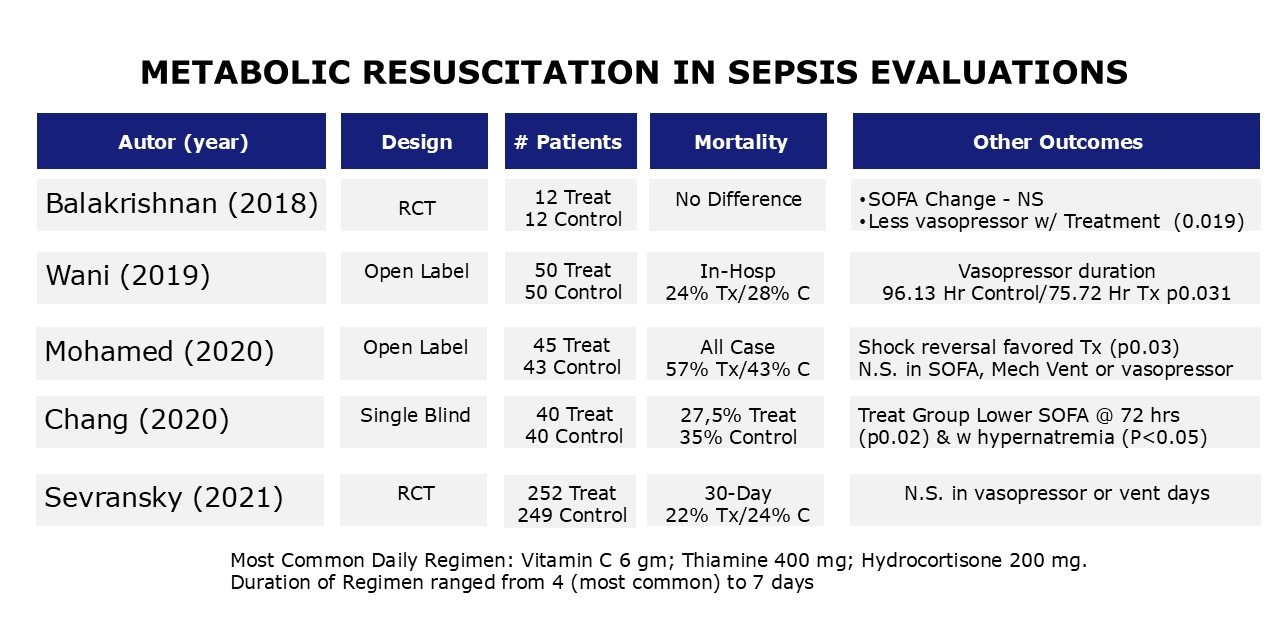
Triple Combination Therapy ( Vitamin C, Corticosteroids and Thiamine (HAT):
- Recent investigations have considered the impact of a combined triple therapy (hydrocortisone, ascorbic acid, and thiamine (HAT) on the progression of sepsis.
- Investigations have produced varying results.
- Studies typically report no change in hospital or ICU mortality.
- Some have found a reduction in the duration of vasopressor use, and or reduction in SOFA score, whereas others have not.
- The combination does not appear to increase the occurrence of adverse events.
CONCLUSIONS:
-
Current Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines recommend:
-
Consider corticosteroid use in sepsis patients with septic shock and ongoing vasopressor needs (weak level recommendation).
-
Against the use of IV Vitamin C (weak level recommendation
-
No recommendation on Metabolic Resuscitation
-
- There does not appear to be a value to Metabolic Resuscitation in sepsis at this time.
To receive articles like these in your Inbox, you can subscribe to Sepsis Program Optimization Insights.
Erkan Hassan is the Co-Founder & Chief Clinical Officer of Sepsis Program Optimization where he designs & oversees the implementation of solutions to optimize sepsis programs.
To discuss your organization’s Barriers of Effective Sepsis Care, contact Erkan by phone (844) 4SEPSIS (844-473-7747), email (erkan@spo.icu), or video chat.





