Sepsis on the Basis of Suspicion of Infection
SUMMARY
- A suspected or documented infection is required for the diagnosis of sepsis.
- The lack of a “gold standard” for sepsis diagnosis coupled with the delay of culture results increases the likelihood of including patients in the sepsis management pathway who do not actually have sepsis.
- With nonspecific findings, sepsis mimics multiple other diseases. Sepsis alone should not be the only consideration in these patients.
- Infectious as well as non-infectious conditions as the patient’s etiology of their acute illness should be sought.
BACKGROUND
- After hospitalization, a patient’s trajectory can rapidly change.
- The recently published Surviving Sepsis Campaign 2021 International guidelines recommend continually assessing the patient to determine if other diagnoses other than sepsis are more or less likely.
- Due to the deficiencies listed above, the occurrence of sepsis might be overestimated.
- Recent Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommendations provide antimicrobial dosing guidance based on the clinical probability of the patient having sepsis.
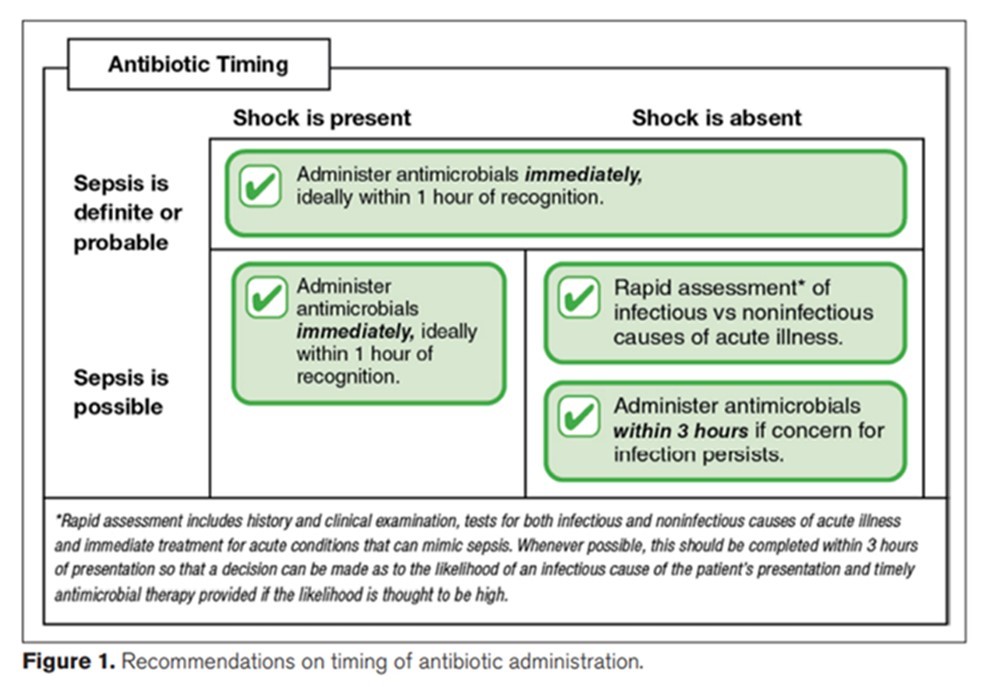
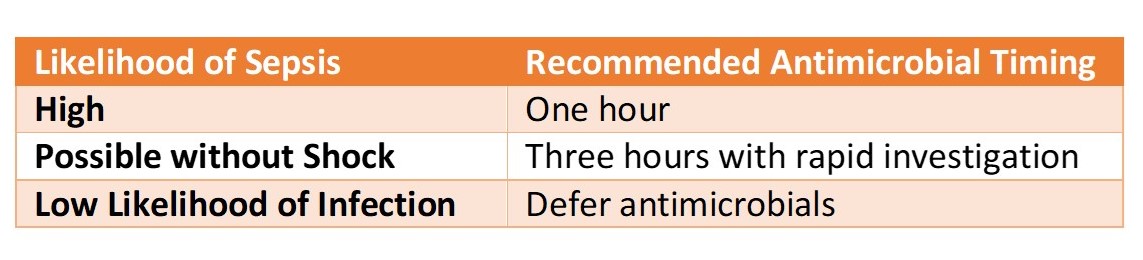
- Unfortunately, there guidance to determine the probability of sepsis has not been a focus of investigation, with no clear guidance.
REVIEW
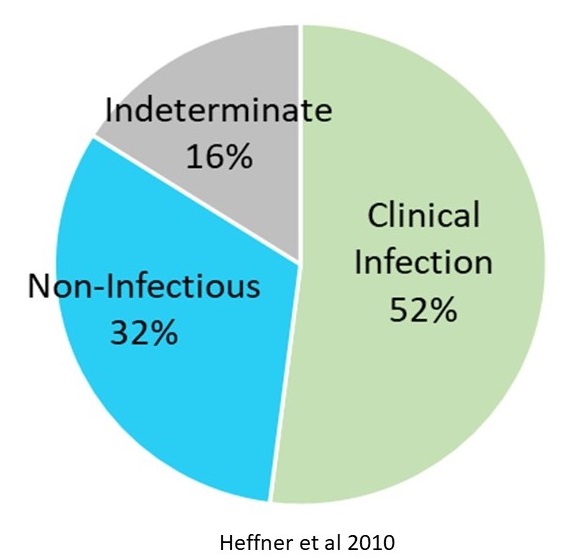
- Heffner et al 2010:
- 211 ED patients with suspected infections – Majority were culture Negative
- 45% (n=95) culture positive
- 55% (n=116) culture negative
- Of the 116 Culture Negative Patients 32% were non-infectious
- 211 ED patients with suspected infections – Majority were culture Negative
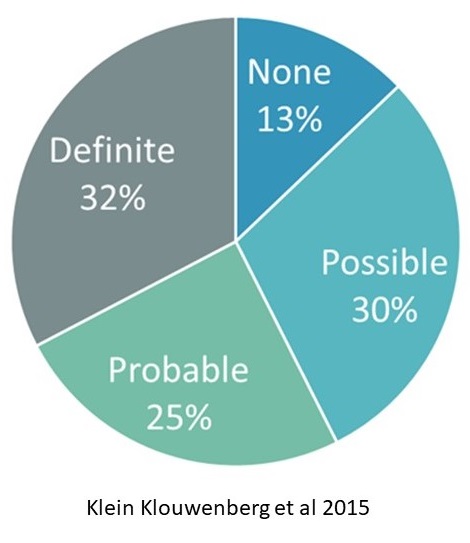
- Klein Klouwenberg et al 2015:
- 2,579 Presumed Sepsis Admissions to ICU
- Clinician review of each case for likelihood of infection
- Criteria defined for:
- No Infection
- Possible
- Probable
- Definite
- 43% of patients were determined to be in the none or possible infection group.
CONCLUSIONS
- Accuracy of the infection diagnosis in patients with suspected sepsis corresponds poorly with the presence of infection either by culture results or clinical definitions.
- 30-40% of patients initially diagnosed with sepsis will have non-infectious conditions.
To receive articles like these in your Inbox, you can subscribe to Sepsis Program Optimization Insights.
Erkan Hassan is the Co-Founder & Chief Clinical Officer of Sepsis Program Optimization where he designs & oversees the implementation of solutions to optimize sepsis programs.
To discuss your organization’s Barriers of Effective Sepsis Care, contact Erkan by phone (844) 4SEPSIS (844-473-7747), email (erkan@spo.icu), or video chat.