Level of Trauma Center Designation and Sepsis Outcomes
SUMMARY:
-
Trauma is a life-threatening complication of sepsis.
-
Mortality is tied to trauma center level designation.
-
Trauma sepsis patients have higher mortality rates than non-sepsis trauma patients.
REVIEW:
- Trauma centers are designated into different levels based on resources, volumes, and commitment to education and research.
- Trauma center levels correlate to injury severity scores and with mortality.
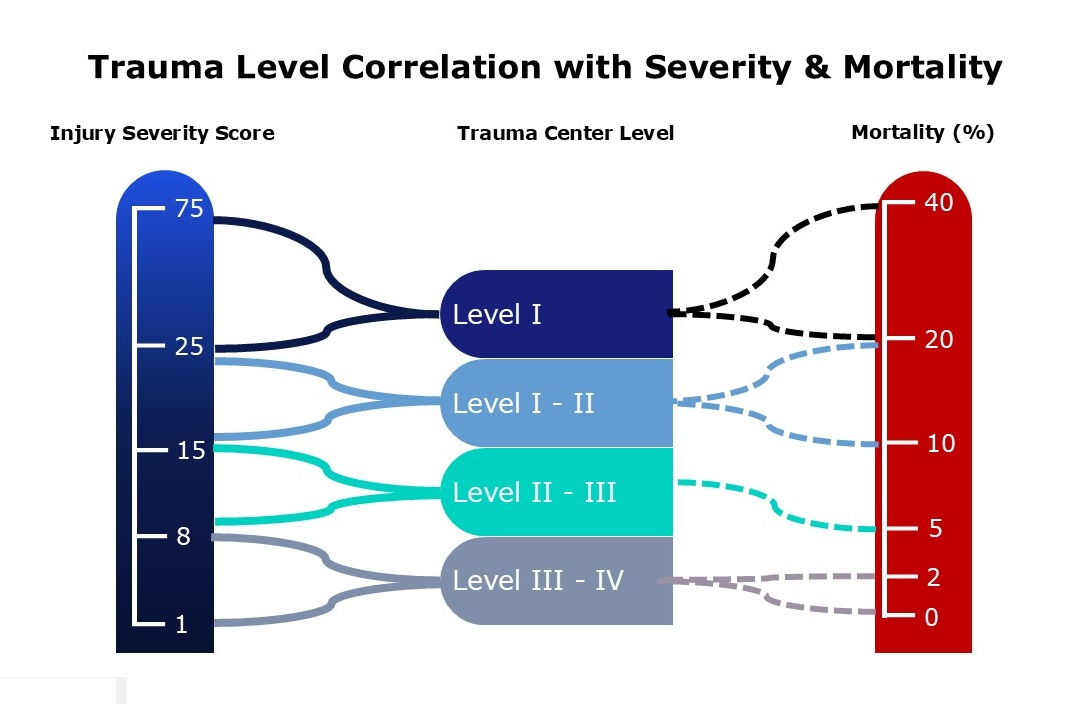
- 60% of trauma deaths occur in the initial hours of hospital admission.
- Sepsis is the most life threatening complication secondary to trauma.
- Approximately 10% of trauma patients develop sepsis, usually within the first few days of admission.
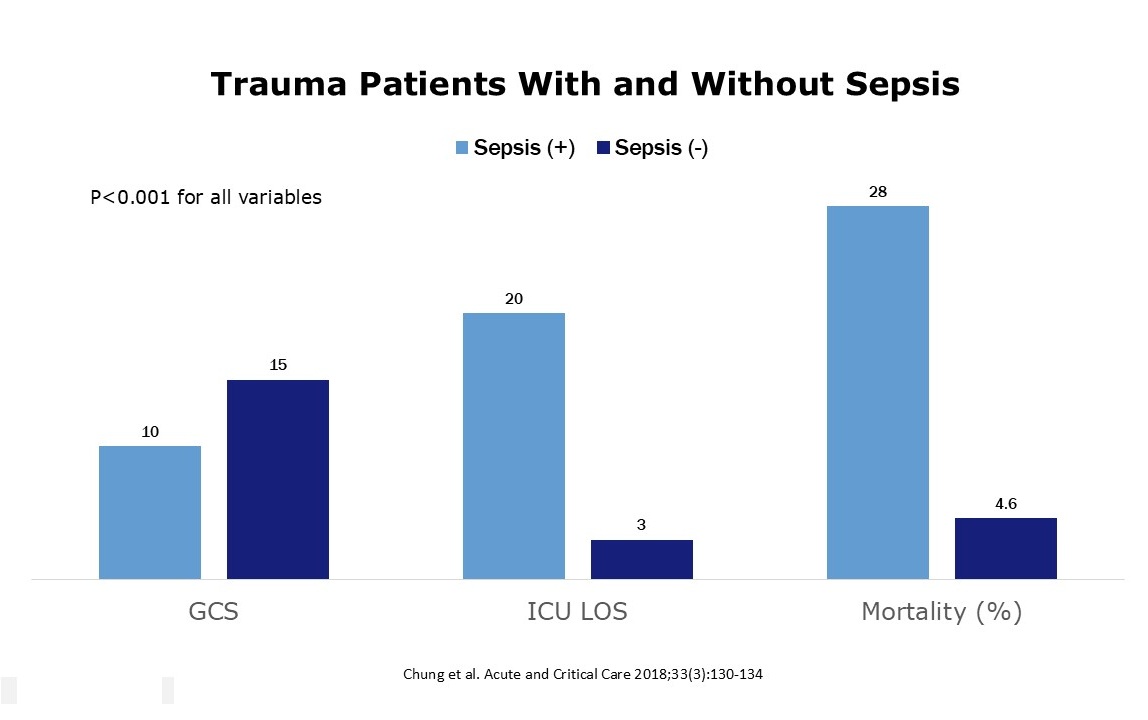
- Trauma patients who develop sepsis have higher mortality rates than those who do not develop sepsis.
- Chung et al. Acute and Critical Care 2018;33(3):130-134
-
- 422 trauma patients
-
- 50 (11.9%) developed sepsis
-
- Sepsis patients were characterized with:
-
-
- Lower GCS scores
-
-
-
- Longer ICU length of stay
-
-
-
- Higher mortality
-
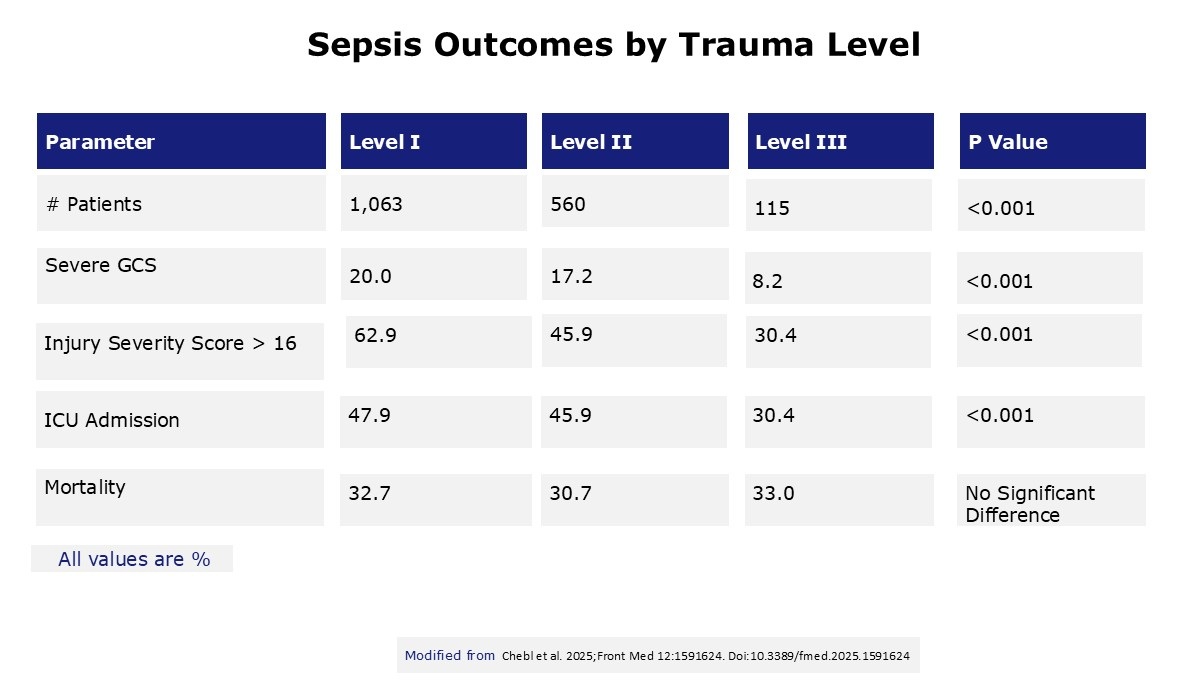
- The incidence of sepsis in trauma patients based on level of trauma center has recently been addressed.
-
- Chebl et al. 2025;Front Med 12:1591624. Doi:10.3389/fmed.2025.1591624
-
- Retrospective cohort of National Trauma Data Bank
-
- 900 trauma centers from 2017
-
- Trauma Level Definitions:
-
-
- I: University based, advanced trauma research
-
-
-
- II: Care for most trauma injuries, potential education & research
-
-
-
- III: Rural community, mild to moderate injuries, transfer of more serious injuries
-
-
- Sepsis-3 definition
-
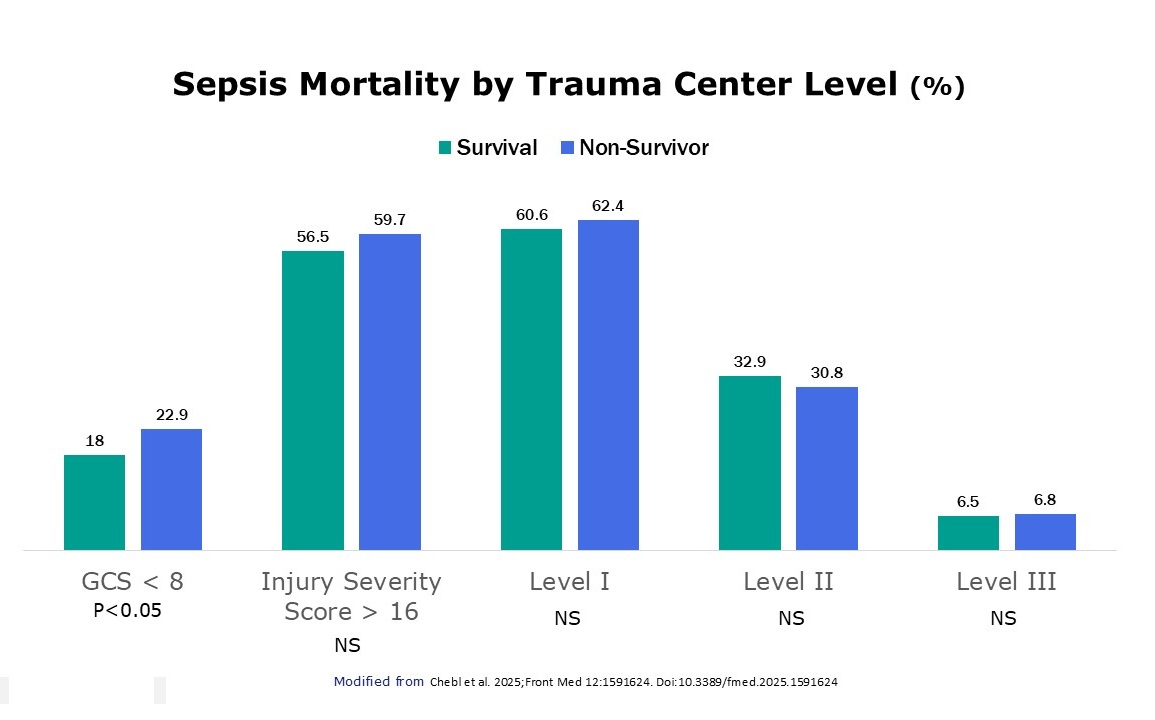
- After adjustment for clinically significant variables (patient demographics, injury, severity score, complications, hospital type), there was no difference in sepsis mortality between the different trauma levels of care.
- The difference between death and survival was not statistically significantly different based on trauma center level.
- Limitations of these findings include:
-
- Small Level III sample size
-
- Unknown sepsis information including: timing of sepsis; fluid resuscitation, antibiotic administration, use of order sets.
- Trauma management focuses on the immediate resuscitation and stabilization.
- If trauma patients survive their initial injury, sepsis identification and management should be a concern across all trauma center levels.
SUMMARY:
- Sepsis occurs in approximately 10% of trauma patients and is a major cause of life-threatening illness.
- Trauma patients with sepsis have a poorer outcome than trauma patients without sepsis.
- Sepsis mortality does not appear to be influenced by the trauma center level designation.
To receive articles like these in your Inbox, you can subscribe to Sepsis Program Optimization Insights.
Erkan Hassan is the Co-Founder & Chief Clinical Officer of Sepsis Program Optimization where he designs & oversees the implementation of solutions to optimize sepsis programs.
To discuss your organization’s Barriers of Effective Sepsis Care, contact Erkan by phone (844) 4SEPSIS (844-473-7747), email (erkan@spo.icu), or video chat.





