Low Agreement in Sepsis Time-Zero Determination
SUMMARY
- Variability in time-zero determination may limit the interpretation of pass/fail sepsis bundle compliance.
- Three different definitions exist to meet time-zero criteria.
- There is wide variability between clinicians and abstractors in determining time-zero with poor interrater reliability.
BACKGROUND
- Sepsis bundle compliance is a timed measure relative to the first point sepsis criteria are met, referred to as “Time-Zero (T-0).1. There are currently three (3) different varying definitions for T-0:
a. In the Emergency Department (ED), T-0 is defined as the time of initial triage.
b. In locations other than the ED, T-0 is the first point sepsis criteria are met based on current Sepsis Guidelines.Specifically:
- Dysregulated host response
- Suspected or documented infection
- Organ dysfunction with SOFA score above 2.
c. CMS SEP-1 Criteria:
- 2 or more systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria
- Suspected or documented infection
- 1 or more organ dysfunction criteria
- Clinician explicitly documents severe sepsis or septic shock (even if the patient does not have objective clinical findings associated with sepsis).
REVIEW
T-0 is a complex definition which could lead to varying interpretations if cases passed or failed meeting sepsis bundle and SEP-1 compliance.
There are several complexities associated with identifying the correct sepsis T-0:
- Up to 53% of patients within the ED do not demonstrate evidence of sepsis at time of triage.
- Hospital abstractors typically must evaluate multiple sources to identify all the data elements required to identify the appropriate T-0
- The actual time of the objective clinical findings associated with sepsis is not necessarily the same time as the recognition of sepsis and initiation of interventions by the bedside clinician.
Given these challenges, it is not surprising there is high variability and frequent disagreement on T-0, especially between abstractors and clinicians.
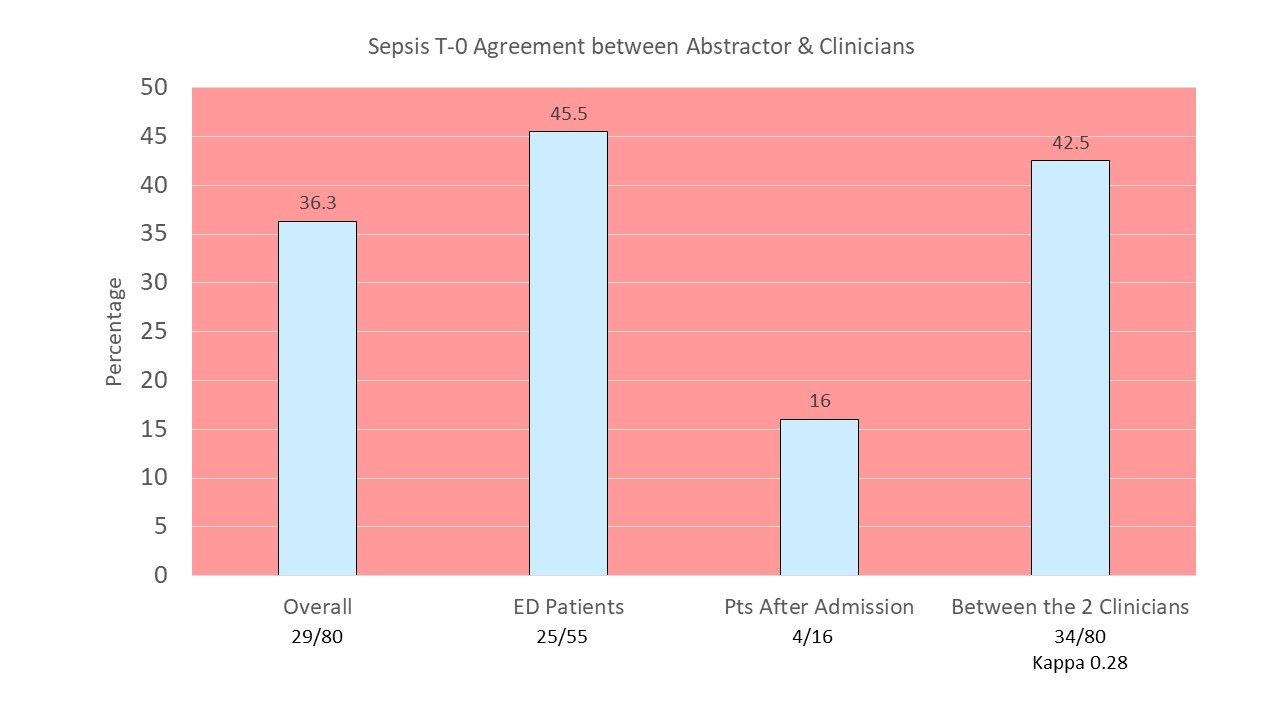
A recent study had 1 abstractor and 2 clinicians independently review 80 sepsis cases to determine T-0 inter-observer variability (Rhee C, et al. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology 2018;0:1-3. Doi:10.1017/ice.2018.134
- CMS SEP-1 sepsis criteria definitions were used for this evaluation.
- Overall, there was a high degree of variability and poor inter-rater reliability on agreement, with an interrater agreement Kappa score of 0.39.
- The median time difference in T-0 between clinicians and abstractor was 40 minutes.
The best agreement on T-0 occurred in the 55 ED patients at 45.5%.
CONCLUSIONS
- Agreement on the definition of T-0 among the 3 evaluations was variable and poor (including between the 2 clinicians).
- Different reviewers may reach different conclusions about T-0 which may alter sepsis bundle compliance metrics.
To receive articles like these in your Inbox, you can subscribe to Sepsis Program Optimization Insights.
Erkan Hassan is the Co-Founder & Chief Clinical Officer of Sepsis Program Optimization where he designs & oversees the implementation of solutions to optimize sepsis programs.
To discuss your organization’s Barriers of Effective Sepsis Care, contact Erkan by phone (844) 4SEPSIS (844-473-7747), email (erkan@spo.icu), or video chat.





