Coronavirus and Sepsis Outcome
SUMMARY
COVID-19 focused approach
For Healthcare Administrators: The largest age groups of developing COVID-19 and those admitted to the hospital are the 20-44 and 65-84 age ranges.
For Providers: Sepsis and mortality is greatest in the subset of patients meeting COVID-19 Critical disease definition
On March 27, 2020, the United States became the country with the greatest number of total coronavirus (COVID-19) cases in the world with almost 86,000 cases. We have learned a lot in the past few weeks about this virus.
This update is to add further clarity to COVID-19 as it relates to sepsis.
OVERVIEW
COVID-19 can present as mild, severe or critical disease:

Median time to ICU admission from onset of symptoms is 9.5 to 10.5 days.
Distribution of U.S. cases analyzed by the CDC show
- Case distribution ranged from less than 20 to over 85 years of age
- The distribution of COVID-19 by age was most common in the 20-44 group, followed by the 65-84 age group.
- These 2 groups also had the largest percentages of patients hospitalized.
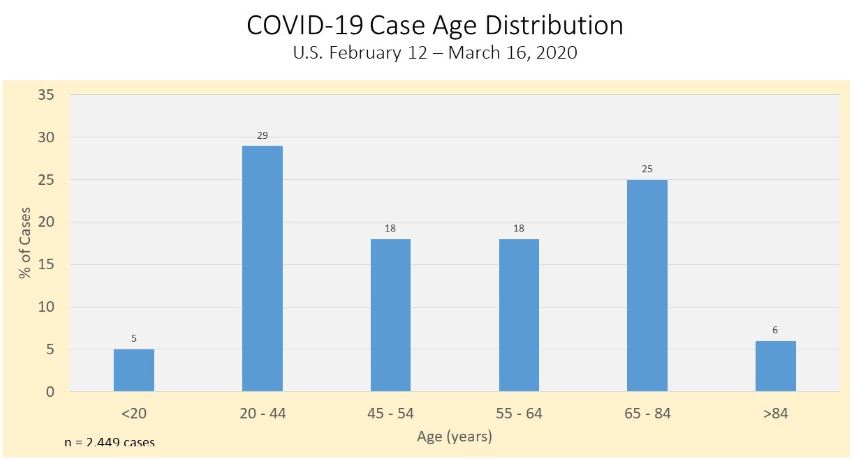
Patients 65 years of age or older accounted for 80% of deaths.
SEPSIS
A recent summary provided key findings from 72,314 cases by the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Infection
- 44,672 confirmed cases
- 16,186 suspected cases
- 10,567 diagnosed cases
- 889 asymptomatic cases
The disease breakdown was:
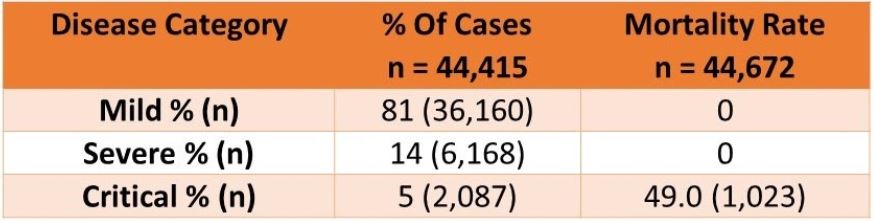
No deaths occurred in patients with mild or severe disease.
Critical disease patients meet the typical criteria for sepsis of dysregulated immune response with at least 1 organ failure due to documented or suspected infection. Although not provided, these patients should meet a SOFA score of 2 or higher.
- 5% of patients manifested critical disease, indicating the need for ICU care.
- Overall mortality was 2.3%.
- 49% of patients with critical disease died
Patients between 70-79 years of age had an 8% mortality rate. Patients over age 80 had a 14.8 % mortality rate..
Analysis of all fatality revealed mortality was elevated in patients with preexisting comorbidities:
- Cardiovascular disease 10.5%
- Diabetes 7.3%
- Chronic respiratory disease 6.3%
- Hypertension 6.0%
- Cancer 5.6%
TREATMENT
- There are no proven or approved treatments for COVID-19. Current treatment is supportive care for ARDS, hypotension and sepsis.
- The Surviving Sepsis Campaign will be publishing COVID-19 recommendations which re-iterate the previously published recommendations.
- They will not recommend protease inhibitors class of antivirals due to the lack of data in the treatment of COVID-19.
- The World Health Organization has launched a multi-country clinical trial evaluating the effect of 4 drug regimens already approved for other illnesses. Ten countries have agreed to participate.
Drug Regimens are:
- Remdesivir
- Lopinavir and ritonavir
- Lopinavir, ritonavir with interferon beta
- Chloroquine
CONCLUSIONS
- Hand washing, social distancing, and self isolation remain the mainstays of our current response.
- Patients within the COVID-19 critical disease category are the subset with mortality. Therefore, providers attempting to improve mortality outcome should focus on patients with critical disease COVID-19.
- Aggressive supportive management to maintain hemodynamic and respiratory function (rehydration, low tidal volume, plateau pressure, PEEP)
To receive articles like these in your Inbox, you can subscribe to Sepsis Program Optimization Insights.
Erkan Hassan is the Co-Founder & Chief Clinical Officer of Sepsis Program Optimization where he designs & oversees the implementation of solutions to optimize sepsis programs.
To discuss your organization’s Barriers of Effective Sepsis Care, contact Erkan by phone (844) 4SEPSIS (844-473-7747), email (erkan@spo.icu), or video chat.