Sepsis Outcomes Associated with Liver Disease
SUMMARY:
-
Although rare, liver failure in sepsis has a profound impact on mortality.
-
Liver disease with sepsis requires more critical care support vs without liver disease.
-
Clinicians should consider liver disease as a variable in sepsis patients moving in the future.
REVIEW:
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, recently renamed steatotic liver disease, may have a significant impact on the course of sepsis due to its association with:
- Low-grade inflammation
- Microvascular endothelial dysfunction
- Insulin resistance;
- Impaired immune response.
- There is limited data on the impact of liver disease on the course of sepsis and its outcomes.
-
There are a number of various liver disease severity scores. These include:
- AST to Platelet Ratio (APRI)
- Fibrosis-4 Index for Liver Fibrosis (FIB-4)
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Score (NAFLD)
- FibroScan AST score (FAST)
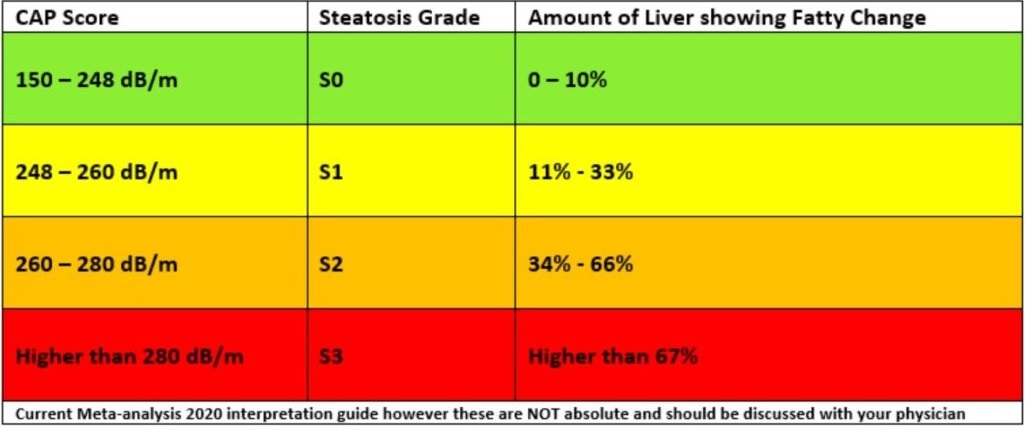
- Controlled Attenuation Parameter (CAP)
- Commonly used to assess steatosis severity
- Various CAP cut points have been used to grade different levels of liver steatosis.
SEPSIS AND LIVER DISEASE:
-
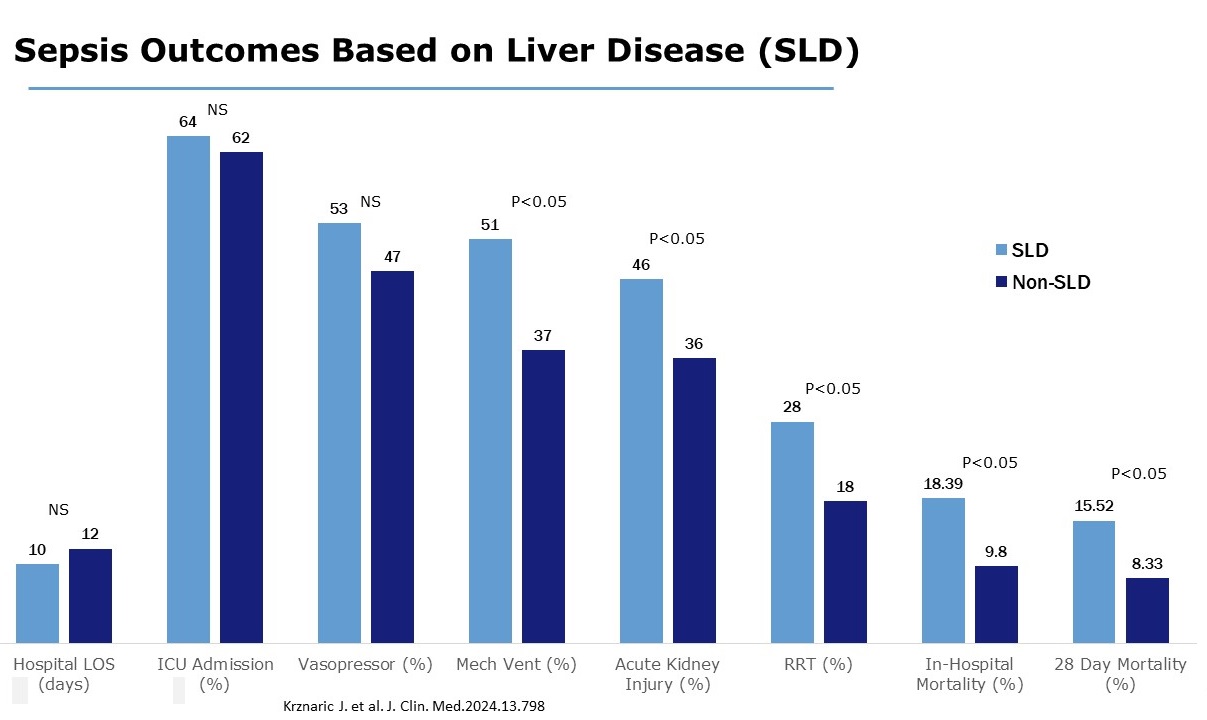
Recent evaluation (Krznaric J, et al Journal of Clinical Medicine;2024:13;798) on the evaluation of hospital mortality rates in 378 patients with sepsis with or without liver disease.
-
No difference between groups in terms of:
- Hospital length of stay
- Need for ICU admission
- Need for vasopressor
- Liver failure patients significantly were:
- Required mechanical ventilation
- Developed acute kidney injury
- Required renal replacement therapy
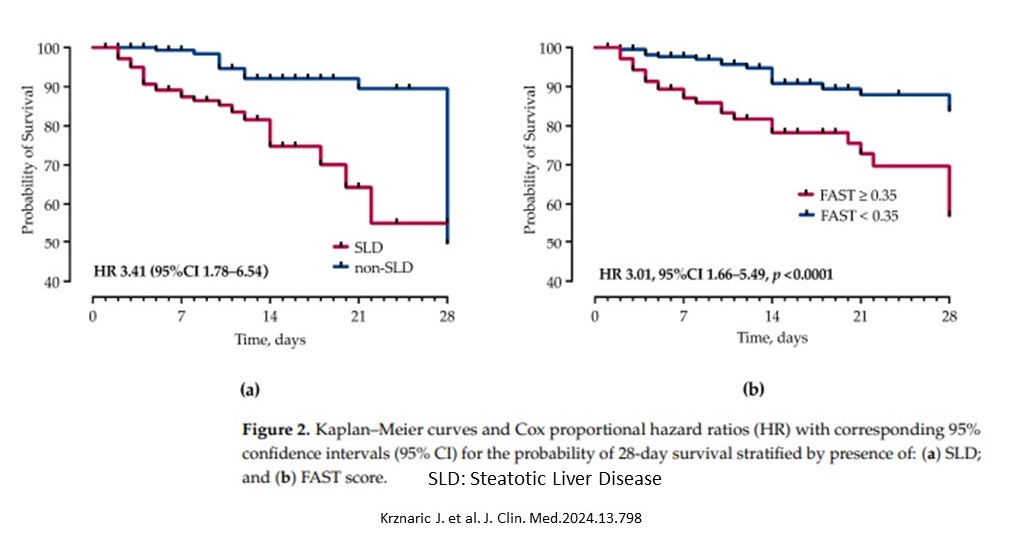
- Mortality was greater in the liver disease patients with a greater 28 day.
-
- Higher mortality was associated with:
- CAP > 270 dB/m
- NAFLD > 1.3
- FIB-4 score > 3.0
- FAST score > 0.35
- Higher mortality was associated with:
CONCLUSIONS:
-
Sepsis associated liver disease has a high morbidity and mortality associated with it.
-
The role of liver disease in severe infections remain unclear, however, liver disease is associated with physiologic changes which could impact the course of sepsis.
-
Liver disease should be a patient variable to consider in future sepsis patients.
To receive articles like these in your Inbox, you can subscribe to Sepsis Program Optimization Insights.
Erkan Hassan is the Co-Founder & Chief Clinical Officer of Sepsis Program Optimization where he designs & oversees the implementation of solutions to optimize sepsis programs.
To discuss your organization’s Barriers of Effective Sepsis Care, contact Erkan by phone (844) 4SEPSIS (844-473-7747), email (erkan@spo.icu), or video chat.