Sepsis Mortality Based on Origin of Source
SUMMARY
- Sepsis sources of infection come from a variety of origins.
- Source control is a major determinant affecting outcomes in patients with sepsis.
- The source of the sepsis origin may partially contribute to varying mortality rates.
- Infection source should be considered in sepsis program development.
REVIEW
- Due to the heterogeneous nature of sepsis, a variety of sources may be the origin of the infection.
- Consistently, the most common source origin is the pulmonary system. However, clinicians also need to consider a number of other sites.
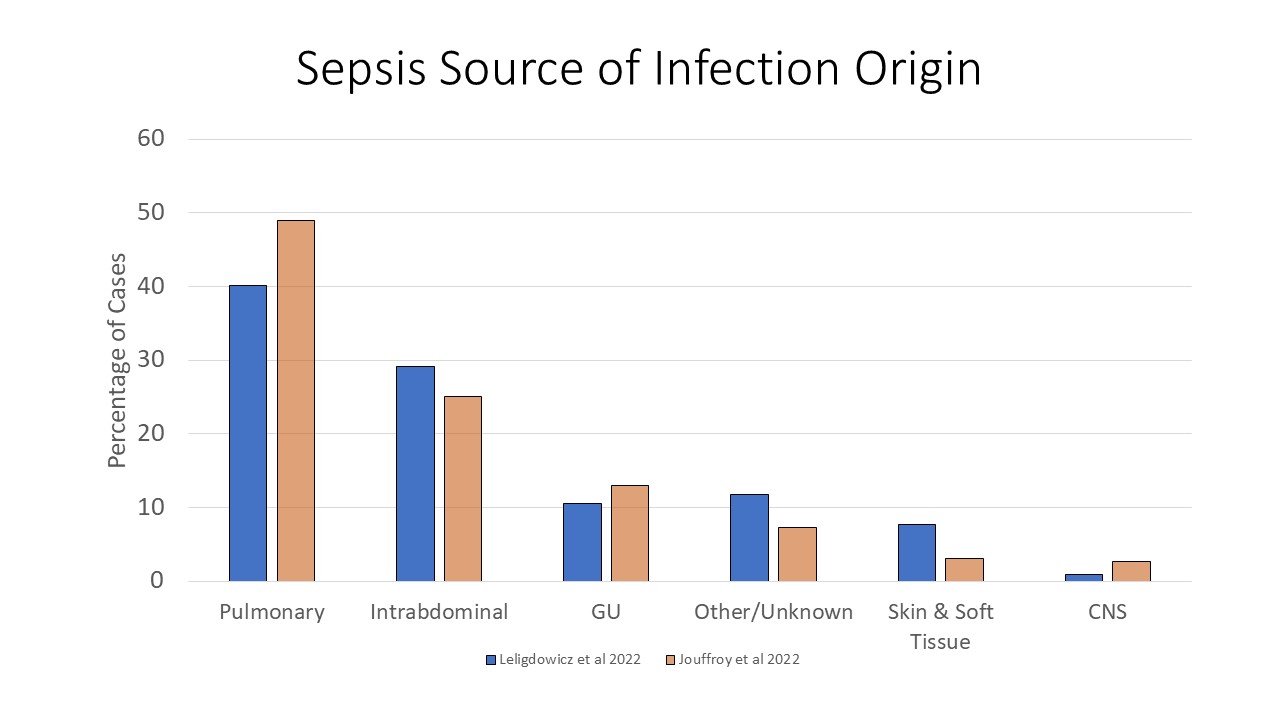
- Recently Prest et al evaluated sepsis patients stratified by the 3 most common sites of infection in over 2.5 million sepsis cases reported through the CDC.
- Pulmonary
- Intraabdominal
- Genitourinary tract
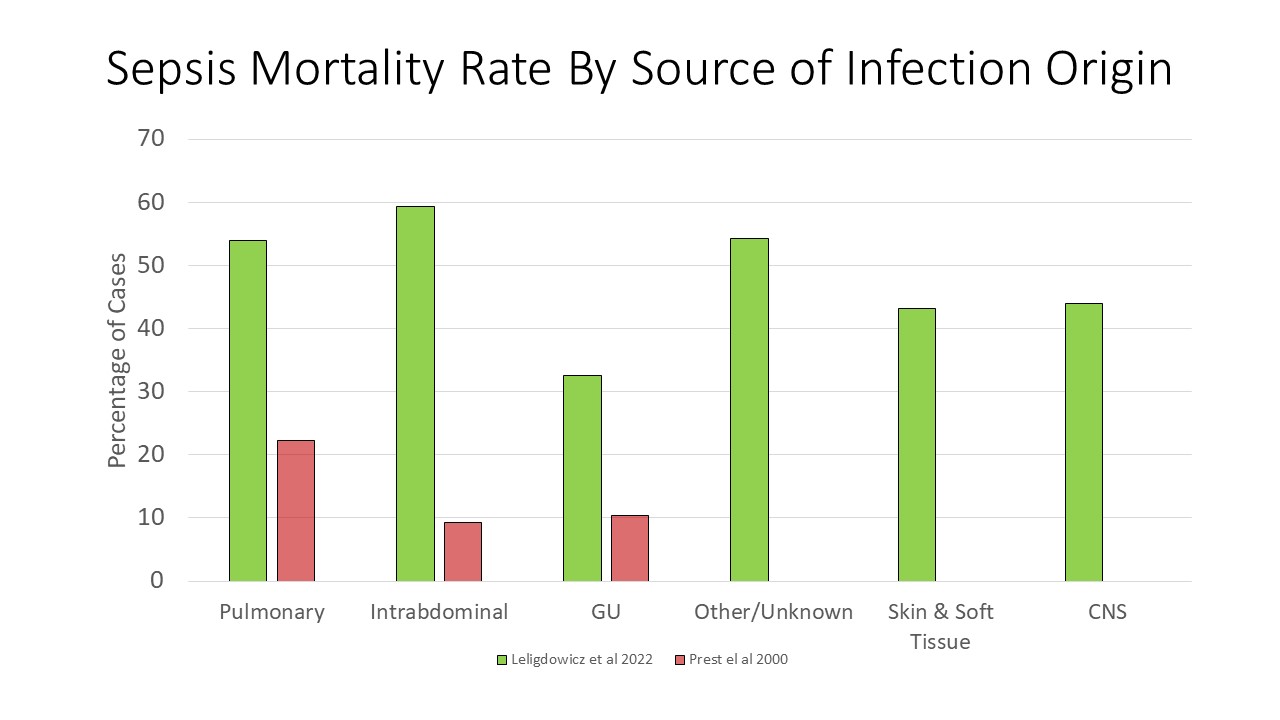
- Pulmonary sepsis patients had the highest mortality rate, followed by GU sepsis, then Intrabdominal sepsis.
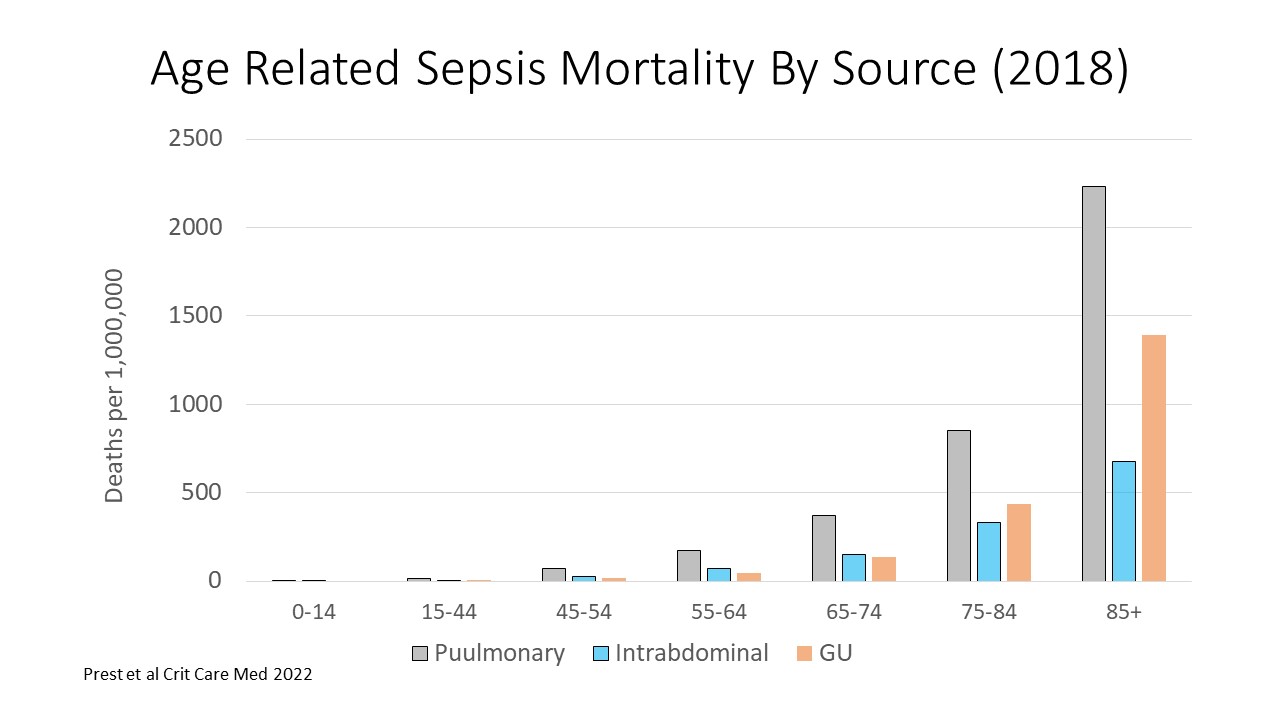
- Males had a significantly higher mortality rate (approximately 26% higher age-adjusted) than females within each source origin.
- Sepsis mortality increase not only by organ system affected, but by increasing age as well.
- Pulmonary remained the leading cause of death by age group as well.
CONCLUSIONS
- The site of infection origin is important ot consider in the effort to combat sepsis.
- The organ affected as well as the patients age should be factors to consider in developing sepsis processes and policies.
To receive articles like these in your Inbox, you can subscribe to Sepsis Program Optimization Insights.
Erkan Hassan is the Co-Founder & Chief Clinical Officer of Sepsis Program Optimization where he designs & oversees the implementation of solutions to optimize sepsis programs.
To discuss your organization’s Barriers of Effective Sepsis Care, contact Erkan by phone (844) 4SEPSIS (844-473-7747), email (erkan@spo.icu), or video chat.





