Prolonged vs Intermittent Antibiotic Infusions
SUMMARY
-
Recent efforts to maximize antibiotic activity have focused on using pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) principles for drug administration.
-
As a preferred choice, beta lactams, and specifically meropenem displays a time dependent bactericidal activity based on free concentrations above the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC).
-
Although additional well controlled studies are needed, it appears prolonged continuous infusions of meropenem provide more favorable outcomes than intermittent infusions.
BACKGROUND
- Effective antibiotic treatment is a crucial aspect of sepsis care.
-
Beta lactams are the most prescribed class of agent in the U.S. with meropenem being a common choice for treatment in ICU patients.
-
The best predictor of antibacterial efficacy is the percentage of the dosing interval with free drug concentrations above the MIC. Beta lactams display this type of time-dependent bactericidal activity and PK/PD characteristics.
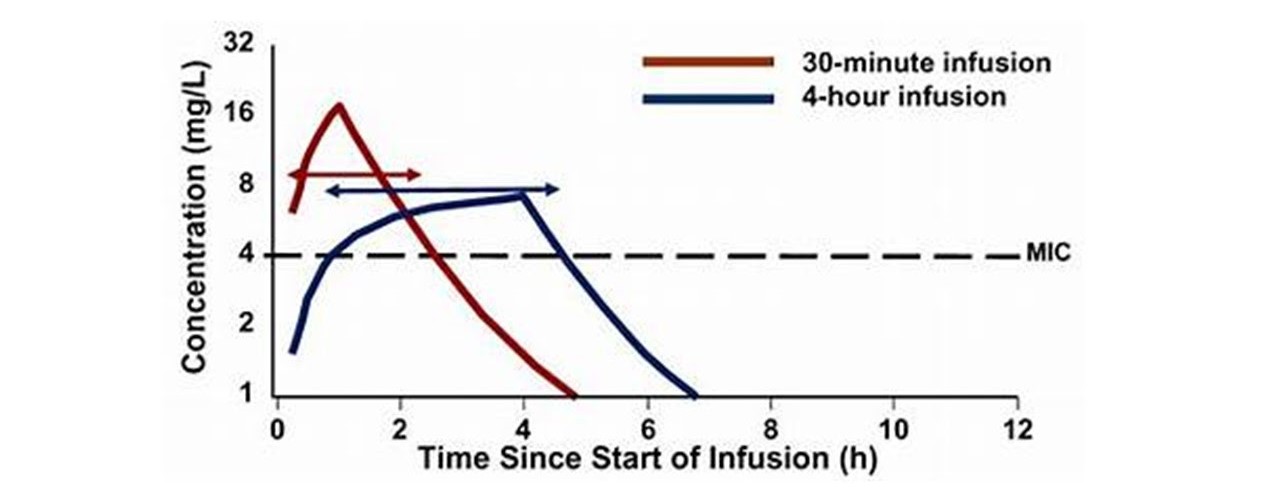
-
Continuous infusion of beta lactams consistently attain the desired drug exposure. However, there is ongoing debate regarding traditional intermittent dosing regimens versus a continuous infusion regimen.
-
Few well controlled studies exist in the evaluation of continuous vs intermittent administration of meropenem on sepsis outcomes.
RESULTS
-
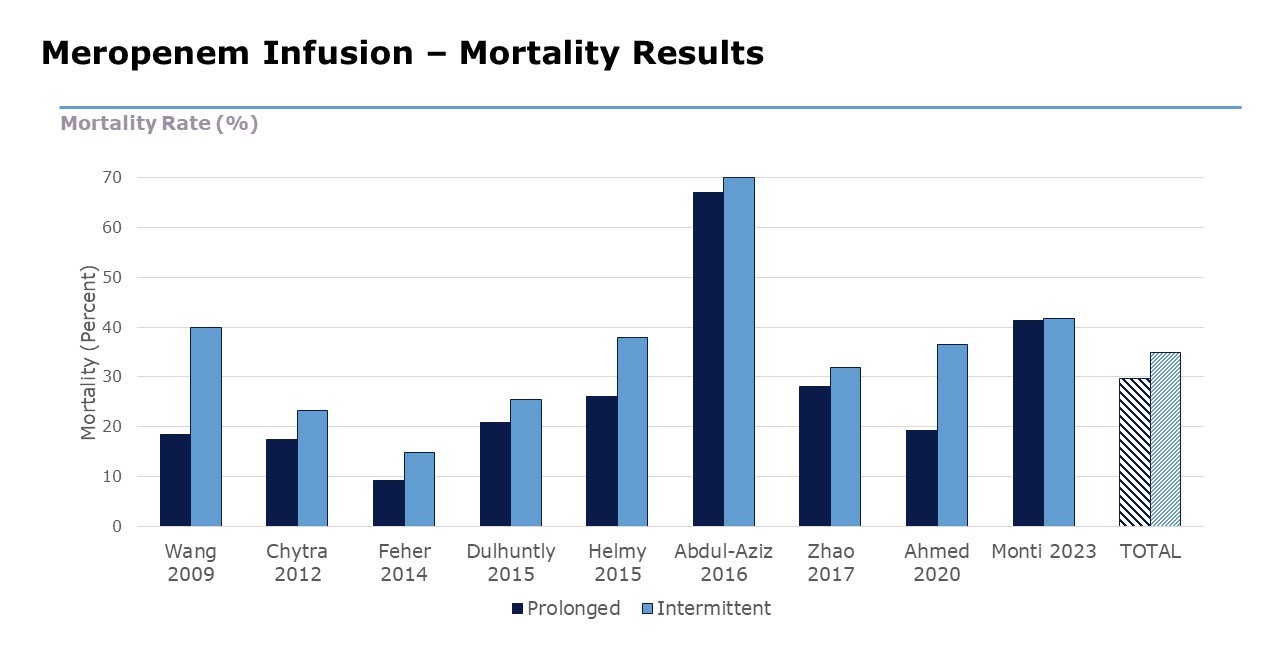
Overall analysis shows that continuous infusion of meropenem is associated with a lower mortality rate than intermittent intravenous infusions.
-
Risk of death was 24-34% lower with continuous infusion vs intermittent.
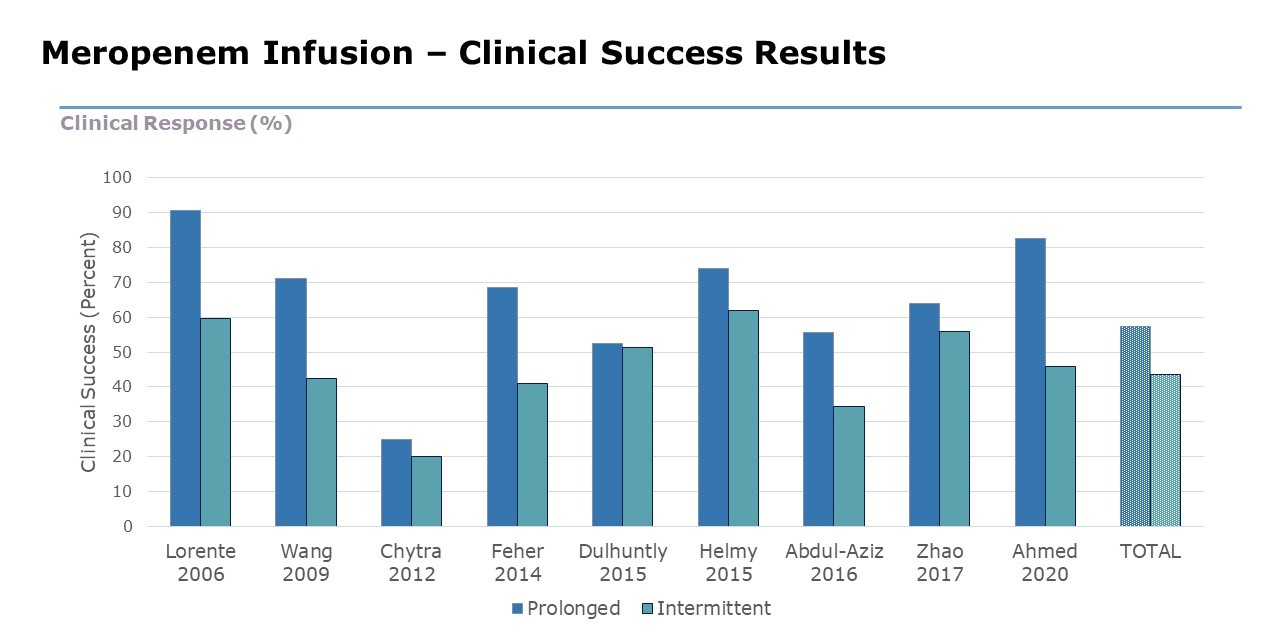
- Clinical success rates were significantly higher in patients receiving prolonged meropenem infusion compared to intermittent infusion.
CONCLUSIONS
-
Evidence from mainly non-randomized studies suggest prolonged/continuous infusion of meropenem could produce superior outcomes in patients with sepsis.
-
Prolonged/continuous infusions offers potential benefits by providing antibiotic concentrations above the MIC.
-
Further research of controlled trials with a larger diverse patient populations are warranted.
To receive articles like these in your Inbox, you can subscribe to Sepsis Program Optimization Insights.
Erkan Hassan is the Co-Founder & Chief Clinical Officer of Sepsis Program Optimization where he designs & oversees the implementation of solutions to optimize sepsis programs.
To discuss your organization’s Barriers of Effective Sepsis Care, contact Erkan by phone (844) 4SEPSIS (844-473-7747), email (erkan@spo.icu), or video chat.