Myocardial Injury in Sepsis
SUMMARY:
-
Sepsis induced myocardial QT prolongation is a serious complication.
-
Sepsis is an independent predictor for the development of prolonged QT interval.
-
New onset QT interval in sepsis had higher arrhythmias and 30 day mortality.
REVIEW:
Liu et al Critical Care 2024;28:115 doi.org/10.1186/s13054-024-
-
Retrospective review of sepsis patients from 2018 – 2022 with sepsis-3 definition.
-
1,024 patients (3.3% from ICU).
-
QT Prolongation (QTP occurred in 235 (22.9%) of patients.
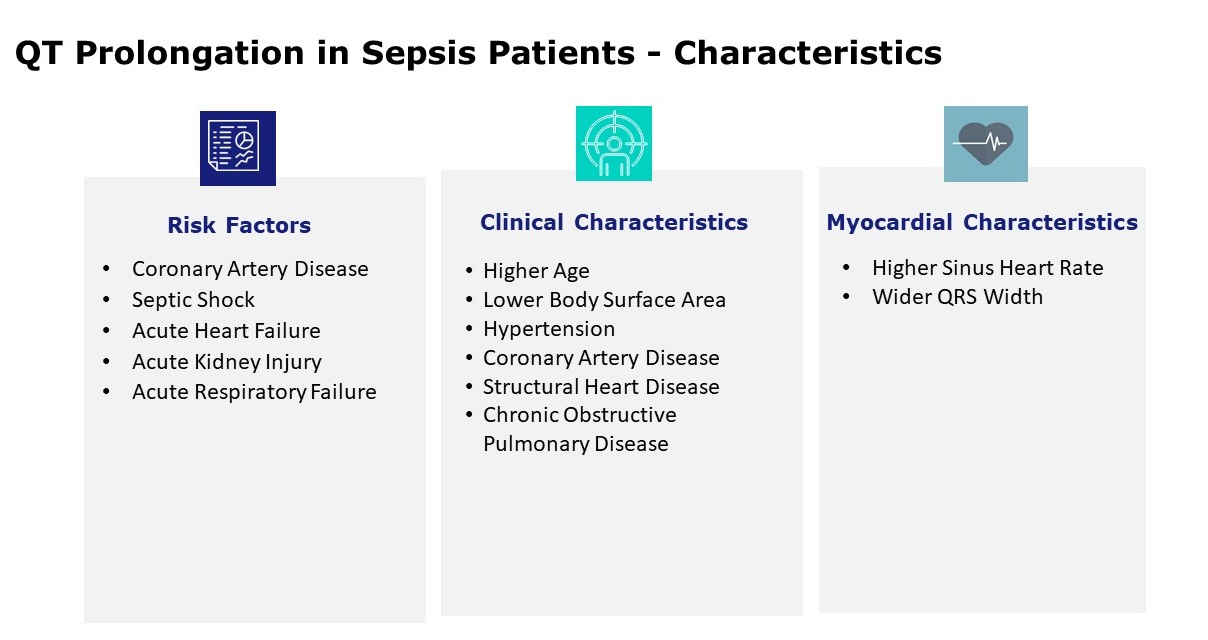
- QTP Risk Factors
-
- Coronary Artery Disease
- Septic Shock
- Acute Heart Failure
- Acute Kidney Injury
- Acute Respiratory Failure
-
QTP was statistically related to:
- Clinical Characteristics
- Higher Age
- Lower Body Surface Area
- Hypertension
- Coronary Artery Disease
- Structural Heart Disease
- Renal Insufficiency
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Clinical Characteristics
-
Myocardial Characteristics
- Higher Sinus Heart Rate
- Wider QRS Width
- Clinical Outcomes
-
- Higher 30-day mortality
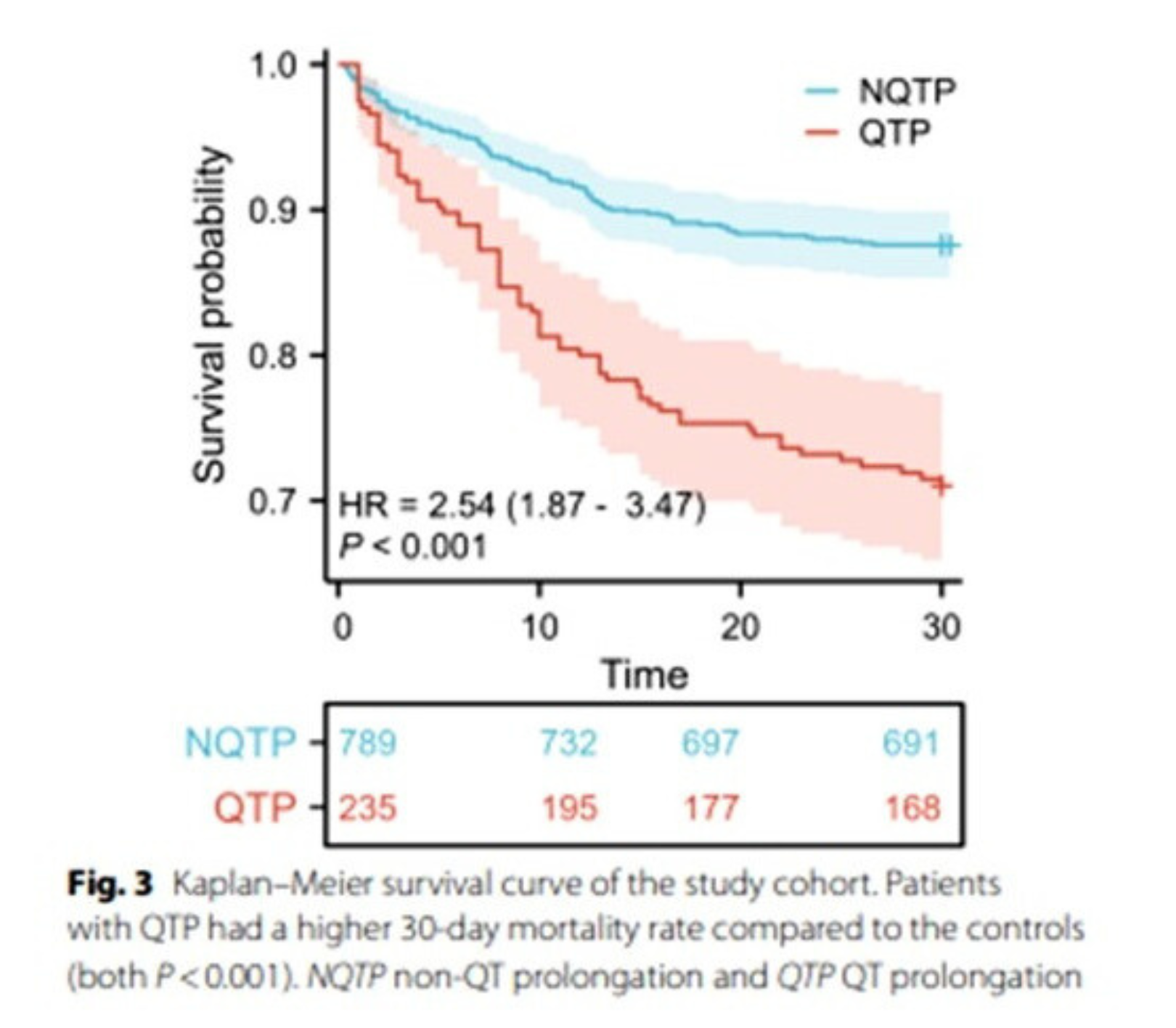
CONCLUSIONS:
-
Occurrence of QTP in sepsis patients is 22.9%.
-
Development of QTP in patients with sepsis is an independent predictor of 30 day mortality.
-
Patients with sepsis and QTP had an increased incidence of atrial and ventricular arrhythmias during hospitalization.
To receive articles like these in your Inbox, you can subscribe to Sepsis Program Optimization Insights.
Erkan Hassan is the Co-Founder & Chief Clinical Officer of Sepsis Program Optimization where he designs & oversees the implementation of solutions to optimize sepsis programs.
To discuss your organization’s Barriers of Effective Sepsis Care, contact Erkan by phone (844) 4SEPSIS (844-473-7747), email (erkan@spo.icu), or video chat.





